Pass4itsure has many years of exam experience! A group of professional Isaca exam experts! Update Isaca CISA test questions throughout the year! The most complete Isaca CISA dumps https://www.pass4itsure.com/cisa.html test questions and answers! The safest buying experience! The biggest free sharing Isaca CISA exam practice questions and answers! Our goal is to help more people pass the exam!
Isaca CISA pdf free download https://drive.google.com/file/d/12T57H4oJ-8K1bmkHN3Gx-DmjGfDEdwNv/view?usp=sharing
Latest Isaca CISA exam dumps pdf [Google Drive]
[Latest PDF] Isaca CISA dumps pdf https://drive.google.com/file/d/12T57H4oJ-8K1bmkHN3Gx-DmjGfDEdwNv/view?usp=sharing
Isaca CISA practice test questions 1-13 free
QUESTION 1
A transaction journal provides the information necessary for detecting unauthorized ___________ (fill in the blank) from
a terminal.
A. Deletion
B. Input
C. Access
D. Duplication
Correct Answer: B
A transaction journal provides the information necessary for detecting unauthorized input from a terminal.
QUESTION 2
Which of the following layer of an enterprise data flow architecture is concerned with basic data communication?
A. Data preparation layer
B. Desktop Access Layer
C. Internet/Intranet layer
D. Data access layer
Correct Answer: C
Internet/Intranet layer ?This layer is concerned with basic data communication. Included here are browser
based user interface and TCP/IP networking.
For CISA exam you should know below information about business intelligence:
Business intelligence(BI) is a broad field of IT encompasses the collection and analysis of information to
assist decision making and assess organizational performance. To deliver effective BI, organizations need
to design and implement a data architecture. The complete data architecture consists of two components
The enterprise data flow architecture (EDFA)
A logical data architecture
Various layers/components of this data flow architecture are as follows:
Presentation/desktop access layer ?This is where end users directly deal with information. This layer
includes familiar desktop tools such as spreadsheets, direct querying tools, reporting and analysis suits offered by vendors such as Congas and business objects, and purpose built application such as balanced
source cards and digital dashboards.
Data Source Layer ?Enterprise information derives from number of sources:
Operational data ?Data captured and maintained by an organization\\’s existing systems, and usually held in
system-specific database or flat files. External Data ?Data provided to an organization by external sources.
This could include data such as customer demographic and market share information.
Nonoperational data ?Information needed by end user that is not currently maintained in a computer
accessible format.
Core data warehouse ?This is where all the data of interest to an organization is captured and organized to
assist reporting and analysis. DWs are normally instituted as large relational databases. A property constituted DW
should support three basic form of an inquiry.
Drilling up and drilling down ?Using dimension of interest to the business, it should be possible to aggregate data as
well as drill down. Attributes available at the more granular levels of the warehouse can also be used to refine the
analysis.
Drill across ?Use common attributes to access a cross section of information in the warehouse such as sum sales
across all product lines by customer and group of customers according to length of association with the company.
Historical Analysis ?The warehouse should support this by holding historical, time variant data. An example of historical
analysis would be to report monthly store sales and then repeat the analysis using only customer who were preexisting
at the start of the year in order to separate the effective new customer from the ability to generate repeat business with
existing customers.
Data Mart Layer ?Data mart represents subset of information from the core DW selected and organized to meet the
needs of a particular business unit or business line. Data mart can be relational databases or some form on-line
analytical processing (OLAP) data structure.
Data Staging and quality layer ?This layer is responsible for data copying, transformation into DW format and quality
control. It is particularly important that only reliable data into core DW. This layer needs to be able to deal with problems
periodically thrown by operational systems such as change to account number format and reuse of old accounts and
customer numbers.
Data Access Layer ?This layer operates to connect the data storage and quality layer with data stores in the data
source layer and, in the process, avoiding the need to know to know exactly how these data stores are organized.
Technology now permits SQL access to data even if it is not stored in a relational database.
Data Preparation layer ?This layer is concerned with the assembly and preparation of data for loading into data marts.
The usual practice is to per-calculate the values that are loaded into OLAP data repositories to increase access speed.
Data mining is concern with exploring large volume of data to determine patterns and trends of information. Data mining
often identifies patterns that are counterintuitive due to number and complexity of data relationships. Data quality needs
to be very high to not corrupt the result.
Metadata repository layer ?Metadata are data about data. The information held in metadata layer needs to extend
beyond data structure names and formats to provide detail on business purpose and context. The metadata layer
should be comprehensive in scope, covering data as they flow between the various layers, including documenting
transformation and validation rules.
Warehouse Management Layer ?The function of this layer is the scheduling of the tasks necessary to build and maintain the DW and populate data marts. This layer is also involved in administration of security.
Application messaging layer ?This layer is concerned with transporting information between the various layers. In
addition to business data, this layer encompasses generation, storage and targeted communication of control
messages.
Internet/Intranet layer ?This layer is concerned with basic data communication. Included here are browser based user
interface and TCP/IP networking.
Various analysis models used by data architects/ analysis follows:
Activity or swim-lane diagram ?De-construct business processes.
Entity relationship diagram ?Depict data entities and how they relate. These data analysis methods obviously play an
important part in developing an enterprise data model. However, it is also crucial that knowledgeable business operative
is involved in the process. This way proper understanding can be obtained of the business purpose and context of the
data. This also mitigates the risk of replication of suboptimal data configuration from existing systems and database into
DW.
The following were incorrect answers:
Desktop access layer or presentation layer is where end users directly deal with information. This layer includes familiar
desktop tools such as spreadsheets, direct querying tools, reporting and analysis suits offered by vendors such as
Congas and business objects, and purpose built application such as balanced source cards and digital dashboards.
Data preparation layer ?This layer is concerned with the assembly and preparation of data for loading into
data marts. The usual practice is to per-calculate the values that are loaded into OLAP data repositories to
increase access speed.
Data access layer ?his layer operates to connect the data storage and quality layer with data stores in the
data source layer and, in the process, avoiding the need to know to know exactly how these data stores
are organized. Technology now permits SQL access to data even if it is not stored in a relational database.
Reference:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 188
QUESTION 3
An IS auditor is reviewing the remote access methods of a company used to access system remotely. Which of the
following is LEAST preferred remote access method from a security and control point of view?
A. RADIUS
B. TACACS
C. DIAL-UP
D. DIAMETER
Correct Answer: C
Dial-up connectivity not based on centralize control and least preferred from security and control
standpoint.
Remote access user can connect remotely to their organization\\’s networks with the same level of
functionality as if they would access from within their office.
In connecting to an organization\\’s network, a common method is to use dial-up lines. Access is granted
through the organization\\’s network access server (NAS) working in concert with an organization network
firewall and router. The NAS handle user authentication, access control and accounting while maintaining
connectivity. The most common protocol for doing this is the Remote Access Dial-In User Service
(RADIUS) and Terminal Access Controller Access Controller System (TACACS).
Remote access Controls include:
Policy and standard
Proper authorization
Identification and authentication mechanism
Encryption tool and technique such as use of VPN
System and network management
Reference:
CISA Review Manual 2014 Page number 334
QUESTION 4
The use of digital signatures:
A. requires the use of a one-time password generator.
B. provides encryption to a message.
C. validates the source of a message.
D. ensures message confidentiality.
Correct Answer: C
The use of a digital signature verifies the identity of the sender, but does not encrypt the whole message, and hence is
not enough to ensure confidentiality. A one-time password generator is an option, but is not a requirement for using
digital signatures.
QUESTION 5
Which of the following cloud computing service model is a provision model in which an organization outsources the
equipment used to support operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components?
A. Software as a service
B. Data as a service
C. Platform as a service
D. Infrastructure as a service
Correct Answer: D
Infrastructure as a Service is a provision model in which an organization outsources the equipment used to support
operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components. The service provider owns the equipment
and is responsible for housing, running and maintaining it. The client typically pays on a per-use basis.
For your exam you should know below information about Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of
configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly
provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes
availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models. Cloud
Computing
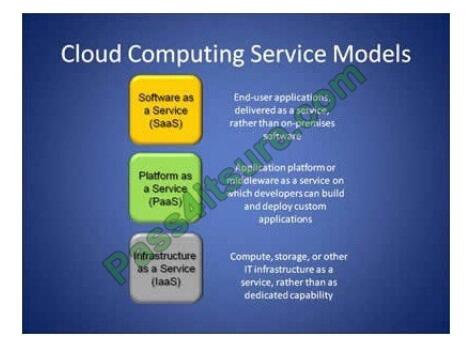
Cloud computing service models: Cloud computing service models
Software as a Service (Seas) Software as a Service (Seas) is a software distribution model in which applications are
hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the Internet.SaaS is
closely related to the ASP (application service provider) and on demand computing software delivery models. IDC
identifies two slightly different delivery models for Seas. The hosted application management (hosted AM) model is
similar to ASP: a provider hosts commercially available software for customers and delivers it over the Web. In the
software on demand model, the provider gives customers network-based access to a single copy of an application
created specifically for Seas distribution.
Provider gives users access to specific application software (CRM, e-mail, games). The provider gives the customers
network based access to a single copy of an application created specifically for Seas distribution and use.
Benefits of the Seas model include:
easier administration
automatic updates and patch management
compatibility: All users will have the same version of software.
easier collaboration, for the same reason
global accessibility.
Platform as a Service (Peas)
Platform as a Service (Peas) is a way to rent hardware, operating systems, storage and network capacity
over the Internet. The service delivery model allows the customer to rent virtualized servers and associated
services for running existing applications or developing and testing new ones.
Cloud providers deliver a computing platform, which can include an operating system, database, and web
server as a holistic execution environment. Where Iasi is the “raw IT network,” Peas is the software
environment that runs on top of the IT network.
Platform as a Service (Peas) is an outgrowth of Software as a Service (Seas), a software distribution
model in which hosted software applications are made available to customers over the Internet. Peas has
several advantages for developers. With Peas, operating system features can be changed and upgraded
frequently. Geographically distributed development teams can work together on software development
projects. Services can be obtained from diverse sources that cross international boundaries. Initial and
ongoing costs can be reduced by the use of infrastructure services from a single vendor rather than
maintaining multiple hardware facilities that often perform duplicate functions or suffer from incompatibility
problems. Overall expenses can also be minimized by unification of programming development efforts.
On the downside, Peas involves some risk of “lock-in” if offerings require proprietary service interfaces or
development languages. Another potential pitfall is that the flexibility of offerings may not meet the needs of
some users whose requirements rapidly evolve.
Infrastructure as a Service (Iasi)
Cloud providers offer the infrastructure environment of a traditional data center in an on-demand delivery
method. Companies deploy their own operating systems, applications, and software onto this provided
infrastructure and are responsible for maintaining them.
Infrastructure as a Service is a provision model in which an organization outsources the equipment used to
support operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components. The service
provider owns the equipment and is responsible for housing, running and maintaining it. The client typically
pays on a per-use basis.
Characteristics and components of Iasi include:
Utility computing service and billing model.
Automation of administrative tasks.
Dynamic scaling.
Desktop virtualization.
Policy-based services.
Internet connectivity.
Infrastructure as a Service is sometimes referred to as Hardware as a Service (HaaS).
The following answers are incorrect:
Data as a service – Data Provided as a service rather than needing to be loaded and prepared on
premises.
Software as a service – Software as a Service (Seas) is a software distribution model in which applications
are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the
Internet. Seas is closely related to the ASP (application service provider) and on demand computing
software delivery models.
Platform as a service – Platform as a Service (Peas) is a way to rent hardware, operating systems, storage
and network capacity over the Internet. The service delivery model allows the customer to rent virtualized
servers and associated services for running existing applications or developing and testing new ones.
Reference:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 102 Official ISC2 guide to CISSP 3rd edition Page number 689
http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Software-as-a-Service
http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Platform-as-a-Service-PaaS
http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Infrastructure-as-a-Service-IaaS
QUESTION 6
Which of the following BEST addresses the availability of an online store?
A. Online backups
B. A mirrored site at another location
C. RAID level 5 storage devices
D. Clustered architecture
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 7
Which of the following is penetration test where the penetration tester is provided with limited or no knowledge of the
target\\’s information systems?
A. External Testing
B. Internal Testing
C. Blind Testing
D. Targeted Testing
Correct Answer: C
Blind Testing refers to the condition of testing when the penetration tester is provided with limited or no
knowledge of the target. Such a testing is expensive, since the penetration tester has to research the
target and profile it based on publicly available information.
For your exam you should know below mentioned penetration types
External Testing -Refers to attack and control circumvention attempts on a target\\’s network perimeter from
outside the target\\’s system is usually the Internet
Internal Testing ?Refers to attack and control circumvention attempt on target from within the perimeter.
The objective is to identify what would occur if the external perimeter was successfully compromised and/
or an authorized user from within the network wanted to compromise security of a specific resource on a
network.
Blind Testing -Refers to the condition of testing when the penetration tester is provided with limited or no
knowledge of the target\\’s information systems. Such a testing is expensive, since penetration tester have to research the target and profile it based on publicly available information.
Double Blind Testing -It is an extension of blind testing, since the administrator and security staff at the
target are also not aware of test. Such a testing can effectively evaluate the incident handling and
response capability of the target.
Targeted Testing ?Refers to attack and control circumvention attempts on the target, while both the
target\\’s IT team and penetration tester are aware of the testing activities. Penetration testers are provided
with information related to target and network design. Additionally, they are also provided with a limited
privilege user account to be used as a starting point to identify privilege escalation possibilities in the
system.
The following were incorrect answers:
External Testing -Refers to attack and control circumvention attempts on a target\\’s network perimeter from
outside the target\\’s system is usually the Internet
Internal Testing ?Refers to attack and control circumvention attempt on target from within the perimeter.
The objective is to identify what would occur if the external perimeter was successfully compromised and/
or an authorized user from within the network wanted to compromise security of a specific resource on a
network.
Targeted Testing ?Refers to attack and control circumvention attempts on the target, while both the
target\\’s IT team and penetration tester are aware of the testing activities. Penetration testers are provided
with information related to target and network design. Additionally, they are also provided with a limited
privilege user account to be used as a starting point to identify privilege escalation possibilities in the
system.
Reference:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 369
QUESTION 8
A project manager of a project that is scheduled to take 18 months to complete announces that the project is in a
healthy financial position because, after 6 months, only one-sixth of the budget has been spent. The IS auditor should
FIRST determine:
A. what amount of progress against schedule has been achieved.
B. if the project budget can be reduced.
C. if the project could be brought in ahead of schedule.
D. if the budget savings can be applied to increase the project scope.
Correct Answer: A
Cost performance of a project cannot be properly assessed in isolation of schedule performance. Cost cannot be
assessed simply in terms of elapsed time on a project. To properly assess the project budget position, it is necessary to
know how much progress has actually been made and, given this, what level of expenditure would be expected. It is
possible that project expenditure appears to be low because actual progress has been slow. Until the analysis of project
against schedule has been completed, it is impossible to know whether there is any reason to reduce budget, if the
project has slipped behind schedule, then not only may there be no spare budget but it is possible that extra expenditure
may be needed to retrieve the slippage. The low expenditure could actually be representative of a situation where the
project is likely to miss deadlines rather than potentially come in ahead of time. If the project is found to be ahead of
budget after adjusting for actual progress, this is not necessarily a good outcome because it points to flaws in the
original budgeting process; and, as said above, until further analysis is undertaken, it cannot be determined whether any
spare funds actually exist. Further, if the project is behind schedule, then adding scope may be the wrong thing to do.
QUESTION 9
The MOST useful technique for maintaining management support for the information security program is:
A. identifying the risks and consequences of failure to comply with standards
B. benchmarking the security programs of comparable organizations
C. implementing a comprehensive security awareness and training program
D. informing management about the security of business operations
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 10
Codes from exploit programs are frequently reused in:
A. trojan horses only.
B. computer viruses only.
C. OS patchers.
D. eavedroppers.
E. trojan horses and computer viruses.
F. None of the choices.
Correct Answer: E
“The term “”exploit”” generally refers to small programs designed to take advantage of a software flaw that has been
discovered, either remote or local. The code from the exploit program is frequently reused in trojan horses and computer
viruses. In some cases, a vulnerability can lie in a certain programs processing of a specific file type, such as a non-executable media file.”
QUESTION 11
Which of the following statement correctly describes the differences between tunnel mode and transport mode of the
IPSec protocol?
A. In transport mode the ESP is encrypted where as in tunnel mode the ESP and its header\\’s are encrypted
B. In tunnel mode the ESP is encrypted where as in transport mode the ESP and its header\\’s are encrypted
C. In both modes (tunnel and transport mode) the ESP and its header\\’s are encrypted
D. There is no encryption provided when using ESP or AH
Correct Answer: A
ESP can be used to provide confidentiality, data origin authentication, connectionless integrity, an anti-replay service (a
form of partial sequence integrity), and (limited) traffic flow confidentiality. The set of services provided depends on
options selected at the time of Security Association (SA) establishment and on the location of the implementation in a
network topology. For your exam you should know the information below about the IPSec protocol:
The IP network layer packet security protocol establishes VPNs via transport and tunnel mode encryption methods.
For the transport method, the data portion of each packet is encrypted, encryption within IPSEC is referred to as the
encapsulation security payload (ESP), it is ESP that provides confidentiality over the process. In the tunnel mode, the
ESP payload and its header\\’s are encrypted. To achieve non-repudiation, an additional authentication header (AH) is
applied.
In establishing IPSec sessions in either mode, Security Associations (SAs) are established. SAs defines which security
parameters should be applied between communicating parties as encryption algorithms, key initialization vector, life
span of keys, etc. Within either ESP or AH header, respectively. An SAs is established when a 32-bit security parameter
index (SPI) field is defined within the sending host. The SPI is unique identifier that enables the sending host to
reference the security parameter to apply, as specified, on the receiving host.
IPSec can be made more secure by using asymmetric encryption through the use of Internet Security Association and
Key Management Protocol/Oakley (ISAKMP/Oakley), which allows automated key management, use of public keys,
negotiation, establishment, modification and deletion of SAs and attributes. For authentication, the sender uses digital
certificates. The connection is made secure by supporting the generation, authentication, distribution of the SAs and the
cryptographic keys.
The following were incorrect answers:
The other options presented are invalid as the transport mode encrypts ESP and the tunnel mode encrypts ESP and its
header\\’s.
Reference: CISA review manual 2014 Page number 353
QUESTION 12
What type of risk results when an IS auditor uses an inadequate test procedure and concludes that material errors do
not exist when errors actually exist?
A. Business risk
B. Detection risk
C. Residual risk
D. Inherent risk
Correct Answer: B
Detection risk results when an IS auditor uses an inadequate test procedure and concludes that material errors do not
exist when errors actually exist.
QUESTION 13
Why does an IS auditor review an organization chart?
A. To optimize the responsibilities and authority of individuals
B. To control the responsibilities and authority of individuals
C. To better understand the responsibilities and authority of individuals
D. To identify project sponsors
Correct Answer: C
The primary reason an IS auditor reviews an organization chart is to better understand the responsibilities and authority
of individuals.
Isaca Certification
CISM Exam:Certified Information Security Manager
Free CISM Exam Practice Question https://www.collection4pdf.com/isaca-cism-exam-dumps-pdf-and-practice-questions-free/
Conclusion:
Free real Isaca CISA exam preparation materials, Isaca CISA practice exam + Isaca CISA pdf dumps. Use them correctly and you will not fail. Get the full Isaca CISA dumps https://www.pass4itsure.com/cisa.html ( Q&As: 3184).
Free Isaca CISA dumps pdf download online!
https://drive.google.com/file/d/12T57H4oJ-8K1bmkHN3Gx-DmjGfDEdwNv/view?usp=sharing
